The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence: Why It Matters Despite Astronomical Odds
Recent research suggests the nearest advanced alien civilization could be approximately 33,000 light-years away, highlighting the extreme rarity of intelligent life in our galaxy. Despite these daunting probabilities, scientists argue that continuing the search for extraterrestrial intelligence remains crucial, as either outcome—discovery or continued silence—would fundamentally reshape our understanding of life's place in the universe. The search itself provides valuable insights into planetary habitability and the conditions necessary for technological civilizations to emerge.
The quest to find intelligent life beyond Earth represents one of humanity's most profound scientific endeavors, yet recent research suggests the odds of success appear vanishingly small. According to new findings presented at the EPSC-DPS2025 Joint Meeting in Helsinki, the nearest technological civilization in the Milky Way could be approximately 33,000 light-years distant—potentially on the opposite side of our galaxy from our solar system.
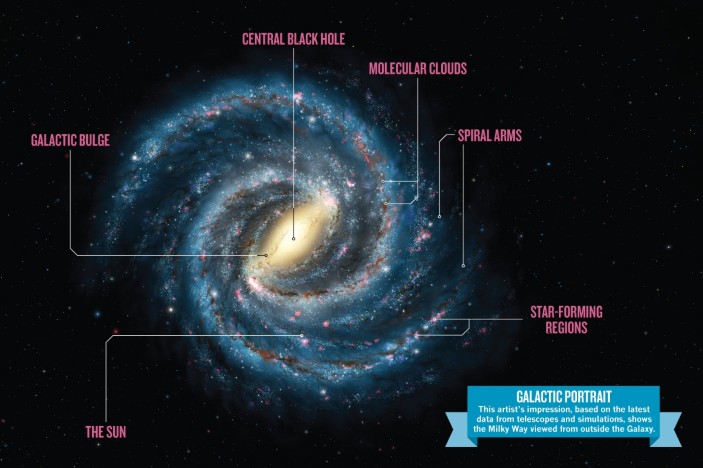
The Astronomical Challenges of Finding ETI
The research conducted by Dr. Manuel Scherf and Professor Helmut Lammer of the Space Research Institute at the Austrian Academy of Sciences reveals the overwhelming challenges in discovering Earth-like planets that possess both the necessary atmospheric conditions and geological processes to support advanced life. Their analysis indicates that for a civilization to exist simultaneously with humanity, it would need to have persisted for at least 280,000 years—and potentially millions of years—to achieve temporal overlap with our own technological era.
Planetary Requirements for Technological Civilization
The emergence of technological civilizations depends on specific planetary conditions that appear exceptionally rare. A planet requires plate tectonics to regulate carbon dioxide through the carbon-silicate cycle, recycling the gas between the atmosphere and the planet's crust. Additionally, atmospheric composition proves critical—planets need at least 18 percent oxygen to support complex animal life and enable open-air combustion necessary for metalworking and technology development.
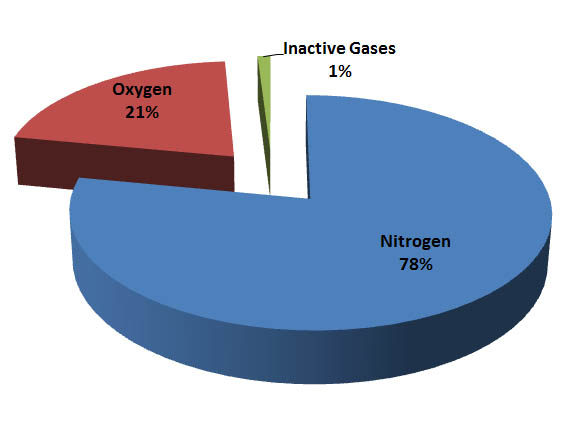
The Significance of Continuing the Search
Despite the apparent rarity of extraterrestrial intelligences (ETIs), scientists emphasize that the search must continue. As Dr. Scherf notes in the research published by Europlanet, "Although ETIs might be rare there is only one way to really find out and that is by searching for it." The scientific value lies in both potential outcomes: discovering extraterrestrial intelligence would represent one of humanity's greatest breakthroughs, while continued absence of detection would reinforce our understanding of life's unique requirements and rarity.
Implications for Humanity's Cosmic Perspective
The estimated 33,000-light-year distance to the nearest potential civilization carries profound implications. Our Sun resides approximately 27,000 light-years from the galactic center, meaning the closest technological civilization might be located on the opposite side of the Milky Way. This vast separation underscores both the immense scale of our galaxy and the potential isolation of technological species within it.

The search for extraterrestrial intelligence transcends mere curiosity about alien life—it represents a fundamental investigation into life's cosmic context. Whether we discover we are not alone or confirm our exceptional rarity, the pursuit reshapes our understanding of life's possibilities and limitations throughout the universe. The continued effort, despite challenging odds, reflects humanity's enduring commitment to exploring our place in the cosmos and understanding the conditions that give rise to technological civilizations.





