Carbon Capture Technology: A Critical Climate Solution
Carbon capture technology represents one of the most promising approaches to addressing climate change by directly removing CO2 from industrial processes and the atmosphere. This innovative technology captures carbon dioxide emissions at their source or directly from the air, preventing them from entering the atmosphere and contributing to global warming. As nations worldwide intensify their climate commitments, carbon capture has emerged as an essential component of comprehensive decarbonization strategies, offering a practical solution for hard-to-abate sectors while supporting the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Carbon capture technology has emerged as a pivotal solution in the global fight against climate change, offering a practical approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from industrial sources and directly from the atmosphere. This innovative technology represents a critical component of comprehensive climate strategies, particularly for sectors where complete decarbonization remains challenging through renewable energy adoption alone.

Understanding Carbon Capture Technology
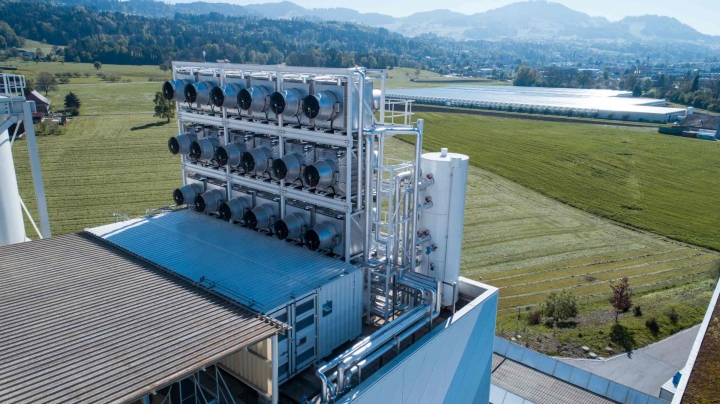
Carbon capture involves the process of capturing carbon dioxide emissions from large point sources such as fossil fuel power plants, industrial processes, or directly from the ambient air. The captured CO2 can then be transported and stored underground in geological formations or utilized in various industrial applications. This technology addresses emissions that would otherwise contribute to atmospheric warming, making it an essential tool for achieving climate targets.
Types of Carbon Capture Methods
Post-Combustion Capture
This method involves capturing CO2 from flue gases after fossil fuels have been burned. Chemical solvents are typically used to separate CO2 from other gases, making it suitable for retrofitting existing power plants and industrial facilities. The technology has seen significant advancements in efficiency and cost reduction in recent years.
Pre-Combustion Capture
Pre-combustion capture involves converting fossil fuels into a mixture of hydrogen and CO2 before combustion occurs. The CO2 is then separated and captured, while the hydrogen can be used as a clean fuel source. This approach is particularly relevant for integrated gasification combined cycle power plants and hydrogen production facilities.

Applications and Implementation
Carbon capture technology finds applications across multiple sectors, including power generation, cement production, steel manufacturing, and chemical processing. These industries represent significant sources of CO2 emissions where alternative decarbonization methods may be limited or economically challenging. The integration of carbon capture systems allows these essential industries to continue operations while dramatically reducing their environmental impact.
Global Significance and Future Outlook
The deployment of carbon capture technology is gaining momentum worldwide as nations recognize its importance in meeting climate commitments. International collaborations and government incentives are driving research, development, and implementation across various regions. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, carbon capture is expected to play an increasingly vital role in global decarbonization efforts, complementing renewable energy adoption and energy efficiency measures.

Carbon capture technology represents a crucial bridge in the transition to a sustainable energy future. While renewable energy sources continue to expand, carbon capture provides an immediate solution for addressing existing emissions from essential industries. As research progresses and implementation scales, this technology will undoubtedly contribute significantly to global climate stabilization efforts, supporting the achievement of international climate targets and creating a more sustainable future for generations to come.